Stock Market Fundamentals: Understanding the Basics of Equity Investing
The stock market is one of the most important components of the modern financial system. It provides a platform where companies raise capital and investors participate in business growth. For beginners, the stock market may appear complex and risky, but understanding its fundamentals can significantly reduce uncertainty and improve decision-making. Stock market fundamentals explain how markets function, why prices change, and how investors can participate responsibly.
A clear grasp of stock market basics is essential for anyone seeking long-term wealth creation, financial independence, or portfolio diversification.
What Is the Stock Market?
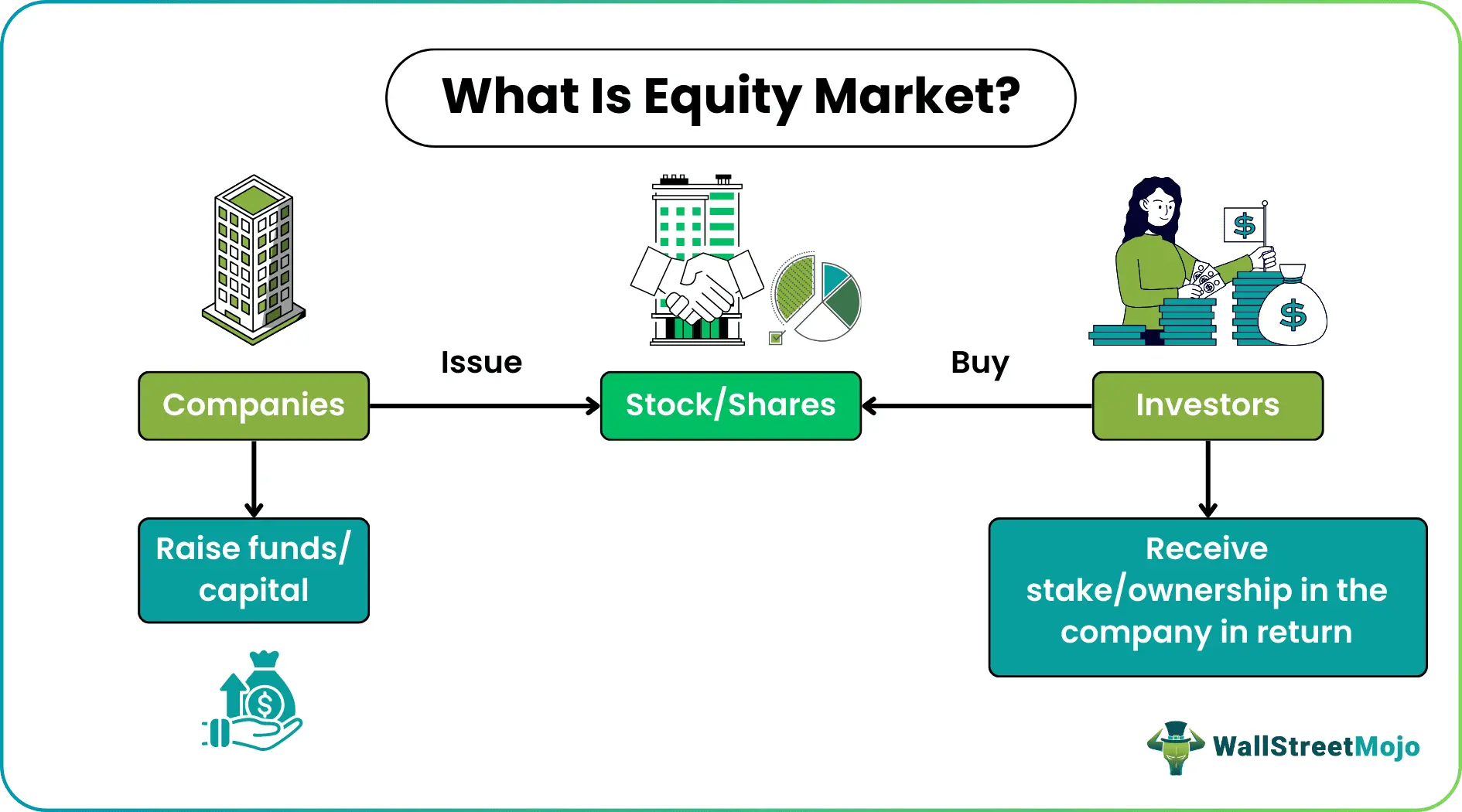
The stock market is a marketplace where shares of publicly listed companies are bought and sold. When a company needs funds to expand operations, develop new products, or reduce debt, it may issue shares to the public. Investors who buy these shares become partial owners of the company.
The stock market serves two primary functions:
- Capital Formation: Companies raise funds for growth and development
- Investment Opportunity: Investors earn returns through dividends and capital appreciation
Stock markets operate through organized exchanges and electronic trading systems that ensure transparency, liquidity, and price discovery.
How the Stock Market Works
The stock market functions on the principle of demand and supply. Share prices fluctuate based on how many investors want to buy or sell a particular stock. When demand exceeds supply, prices rise; when supply exceeds demand, prices fall.
Transactions occur through intermediaries such as brokers, who execute buy and sell orders on behalf of investors. Modern stock markets rely heavily on technology, enabling real-time trading and instant access to market information.
Primary and Secondary Markets
Primary Market
The primary market is where new securities are issued for the first time. Companies raise capital through public offerings, allowing investors to purchase shares directly from the issuer. Funds raised in the primary market go to the company.
Secondary Market
The secondary market is where existing shares are traded among investors. Stock exchanges operate in the secondary market, providing liquidity and continuous pricing. Most investors participate in the secondary market.
Types of Stocks
Equity Shares
Equity shares represent ownership in a company. Equity shareholders may receive dividends and benefit from price appreciation. However, returns are not guaranteed and depend on company performance and market conditions.
Preference Shares
Preference shares offer fixed dividends and priority over equity shareholders in dividend payments and liquidation. However, they usually do not carry voting rights.
Understanding stock types helps investors align investments with income and growth objectives.
Key Participants in the Stock Market
Several participants contribute to the efficient functioning of the stock market:
- Investors: Individuals and institutions investing for returns
- Traders: Market participants seeking short-term price movements
- Companies: Entities raising capital through share issuance
- Brokers: Intermediaries facilitating trades
- Regulators: Authorities ensuring fair practices and investor protection
Each participant plays a vital role in maintaining market stability and integrity.
Stock Market Indices
Stock market indices measure the performance of a group of selected stocks representing a market or sector. Indices act as benchmarks for evaluating market trends and portfolio performance.
Indices help investors understand overall market direction and economic sentiment. A rising index generally indicates economic optimism, while a falling index may signal uncertainty or slowdown.
Factors Influencing Stock Prices
Stock prices are influenced by a combination of internal and external factors:
- Company Performance: Earnings, revenue growth, and profitability
- Economic Conditions: Inflation, interest rates, and economic growth
- Market Sentiment: Investor confidence, expectations, and emotions
- Industry Trends: Technological changes and competitive dynamics
- Global Events: Geopolitical developments and global market movements
Understanding these factors enables investors to interpret price movements more accurately.
Risk and Return in the Stock Market
The stock market operates on the principle of risk and return. Stocks generally offer higher potential returns compared to fixed-income instruments, but they also carry higher risk.
Common stock market risks include:
- Market Risk: Price fluctuations due to overall market movements
- Business Risk: Poor company performance
- Liquidity Risk: Difficulty selling shares quickly
- Volatility Risk: Sharp short-term price changes
Managing risk through diversification and long-term investing is a fundamental principle of stock market participation.
Long-Term Investing vs Short-Term Trading
Long-Term Investing
Long-term investing focuses on holding quality stocks over extended periods to benefit from business growth and compounding. This approach reduces the impact of short-term volatility and supports wealth creation.
Short-Term Trading
Short-term trading aims to profit from price fluctuations over short durations. While it may offer quick gains, it involves higher risk, frequent transactions, and requires strong market knowledge and discipline.
For most beginners, long-term investing is considered more suitable and sustainable.
Importance of Fundamental Analysis
Fundamental analysis evaluates a company’s financial health, business model, management quality, and growth potential. Key aspects include:
- Revenue and profit trends
- Balance sheet strength
- Competitive position
- Industry outlook
Fundamental analysis helps investors determine whether a stock is fairly valued and suitable for long-term investment.
Role of Diversification
Diversification involves spreading investments across multiple stocks, sectors, or asset classes to reduce risk. A diversified portfolio minimizes the impact of poor performance in any single investment and improves overall stability.
Diversification is a core principle of sound stock market investing and portfolio management.
Stock market fundamentals provide the foundation for informed and disciplined investing. By understanding how the stock market works, the types of stocks available, factors affecting prices, and the relationship between risk and return, investors can make rational decisions aligned with their financial goals.
The stock market rewards patience, knowledge, and consistency rather than speculation. With a strong understanding of fundamentals and a long-term perspective, investors can use the stock market as a powerful tool for wealth creation and financial growth.