Corporate Finance
Corporate finance is a core area of finance that focuses on how corporations manage their financial resources to achieve strategic objectives and maximize shareholder value. It deals with critical decisions related to funding, investing, and distributing profits while balancing risk and return. Effective corporate finance management ensures that a company remains profitable, competitive, and financially sustainable in both the short and long term.
In today’s dynamic business environment, corporate finance plays a vital role in guiding organizations through expansion, restructuring, and value creation. This article provides an in-depth overview of corporate finance, its objectives, and its major functional areas, including capital budgeting, mergers and acquisitions, financing decisions, working capital management, and dividend policy.
Meaning and Scope of Corporate Finance
Corporate finance refers to the financial activities associated with running a corporation. Its primary focus is on making optimal financial decisions that enhance firm value. These decisions revolve around three fundamental questions:
- Where should the company invest its funds?
- How should these investments be financed?
- How should profits be distributed among shareholders?
The scope of corporate finance extends across all levels of management, from day-to-day financial operations to long-term strategic planning. It integrates financial analysis, forecasting, risk management, and performance evaluation to support informed decision-making.
Objective of Corporate Finance
The primary objective of corporate finance is the maximization of shareholder wealth. This does not simply mean increasing short-term profits, but enhancing the long-term market value of the company’s shares. Corporate finance decisions aim to balance profitability with risk, liquidity, and growth.
Secondary objectives include maintaining adequate liquidity, ensuring financial stability, minimizing the cost of capital, and supporting sustainable business expansion. Ethical financial practices and regulatory compliance also form an essential part of modern corporate finance.
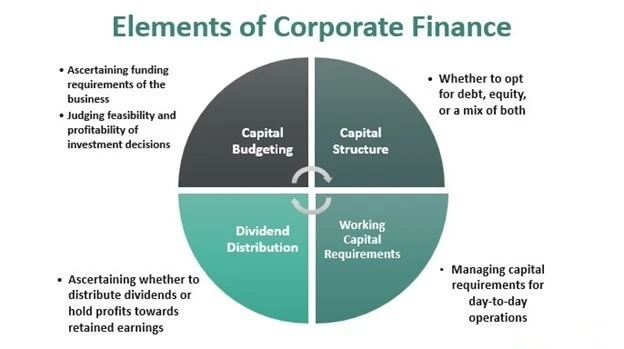
Capital Budgeting: Investment Decision-Making
Capital budgeting is one of the most important functions of corporate finance. It involves evaluating and selecting long-term investment projects such as new plants, machinery, technology upgrades, or product expansions. These decisions require significant capital and have a long-lasting impact on the company’s future performance.
Common capital budgeting techniques include net present value (NPV), internal rate of return (IRR), payback period, and profitability index. The goal is to invest in projects that generate returns higher than the company’s cost of capital, thereby increasing firm value. Sound capital budgeting ensures efficient allocation of scarce financial resources.
Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A)
Mergers and acquisitions are strategic corporate finance activities aimed at business growth, market expansion, diversification, or achieving operational synergies. A merger combines two companies into a single entity, while an acquisition involves one company purchasing another.
Corporate finance professionals play a crucial role in M&A by valuing target companies, structuring deals, arranging financing, and assessing financial risks. Successful M&A transactions can enhance competitive advantage, increase market share, and improve profitability. However, poor valuation or integration can destroy shareholder value, making financial analysis essential.
Debt and Equity Financing
Financing decisions determine how a company raises funds to finance its operations and investments. The two primary sources of financing are debt and equity. Debt financing involves borrowing funds through loans or bonds, while equity financing involves issuing shares to investors.
Corporate finance aims to determine the optimal capital structure, which is the right mix of debt and equity that minimizes the cost of capital and maximizes firm value. Excessive debt increases financial risk, while excessive equity may dilute ownership and reduce earnings per share. Balancing these sources is a critical strategic decision.
Working Capital Management
Working capital management focuses on managing short-term assets and liabilities to ensure smooth business operations. It includes the management of cash, inventory, accounts receivable, and accounts payable.
Efficient working capital management ensures that a company has sufficient liquidity to meet its short-term obligations without holding excessive idle resources. Poor working capital management can lead to cash flow problems, even if the company is profitable on paper. Therefore, maintaining an optimal level of working capital is essential for operational efficiency and financial stability.
Dividend Policy
Dividend policy refers to the decision regarding how much profit a company distributes to shareholders as dividends and how much it retains for reinvestment. This is a critical corporate finance decision, as it directly affects shareholder satisfaction and future growth.
Companies with stable earnings may follow a regular dividend policy, while growth-oriented firms often retain profits to finance expansion. Corporate finance seeks to design a dividend policy that balances shareholder expectations with the company’s long-term funding requirements.
Role of Corporate Finance in Strategic Planning
Corporate finance is closely linked with strategic planning and business decision-making. Financial managers analyze market conditions, assess financial risks, and support management in making informed strategic choices. Whether entering new markets, launching products, or restructuring operations, corporate finance provides the financial framework for strategic initiatives.
Through financial modeling and forecasting, corporate finance helps organizations anticipate future challenges and opportunities, enabling proactive decision-making.
Importance of Corporate Finance
Corporate finance is essential for sustainable business growth and value creation. It ensures efficient use of financial resources, supports strategic investments, and maintains investor confidence. Strong corporate finance practices also improve transparency, governance, and compliance, which are increasingly important in global markets.
In competitive industries, companies with effective corporate finance management are better positioned to adapt to economic changes, manage risks, and capitalize on growth opportunities.
Corporate finance is the backbone of modern business management. By guiding investment decisions, financing strategies, and profit distribution, it plays a crucial role in maximizing shareholder value and ensuring long-term sustainability. Key areas such as capital budgeting, mergers and acquisitions, debt and equity financing, working capital management, and dividend policy collectively shape a company’s financial health. A well-structured corporate finance strategy not only drives profitability but also builds resilience and trust in an ever-evolving business environment.